Sir Peter Higgs
The Higgs boson (named after Peter Higgs CH FRS) is predicted by the Standard Model (SM) of particle physics. The SM successfully accounts for the weak, strong and electromagnetic interactions. The need for a particle with the properties of the Higgs arises from the mathematics behind our current understanding of the electroweak forces and in particular the fact that the W and Z bosons, which mediate the weak force, have large masses. The interaction of other standard model particles with the Higgs field is thought to be the origin of the mass of those particles. The discovery of the Higgs boson with the correct properties, the final step, marks the triumph of the standard model as the theory which united the weak, strong and electromagnetic forces (but no gravitational force as of yet).
The Standard Model of particle physics is at present our best theory for explaining how the universe works on a fundamental level. It describes the interactions of the fundamental particles via three of the four fundamental forces.
The particles are divided into two groups, bosons and fermions. The fermions (spin-half particles) are "matter" particles which make up the elements around us and are further divided into quarks and leptons. The quarks are the constituents of hadrons, such as the proton and neutron, whilst the electron is an example of a lepton. The bosons are sometimes referred to as the "force carriers" and are responsible for the forces between particles. A force carrier is exchanged between two particles, transferring momentum and causing an interaction. The final particle is the Higgs boson, which is intimately linked to why particles have mass. See the chart below for a summary of these particles.
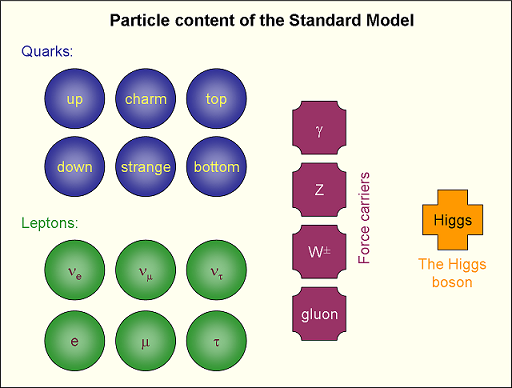
It is important to realize that all the matter of our everyday world is comprised of electrons, up-quarks, down-quarks and photons and gluons which hold them together. All the other particles of the standard model can only be observed in accelerator experiments or in cosmic ray showers.
The three forces described by the Standard Model are:
- Electromagnetism: This force
affects particles which have electric charge, such as the electron,
and is responsible for both electricity and magnetism. In the Standard
Model, it is described by the theory of Quantum ElectroDynamics (QED),
where the force is passed from one particle to another by exchanging
a photon (a particle of light).
- The strong force: This force
is felt by particles which have "colour" charge, such as quarks.
It is responsible for holding together three quarks to form a proton
or neutron. The proton consists of two up quarks and a down quark, while
the neutron is two down quarks with an up quark. This force is mediated
by the exchange of gluons and is described by the theory of Quantum
ChromoDynamics (QCD).
- The weak force: This force is not so apparent in everyday life as the other three. It is manifest in radioactive decays, for example, where a neutron decays to a proton, electron and neutrino. It is mediated by the exchange of W and Z bosons. Unlike all other force carriers, the W boson has a charge of plus or minus 1. This force is unusual because the W and Z bosons are rather heavy, making them difficult to produce and the force very short range. It is believed that the Higgs boson is linked to their mass, as explained by the Higgs mechanism of Electroweak Symmetry breaking, but this has not yet been experimentally confirmed. The weak force is the only force via which neutrinos can interact.
The remaining force, the force of Gravity is absent from the Standard Model. It is very much weaker than the other three and is not relevant to the interactions of particles which can be produced at current high energy physics colliders.
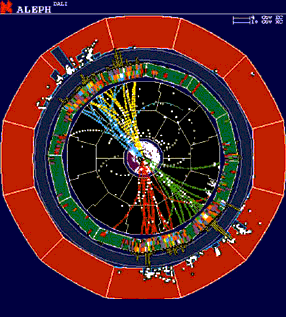 Higgs candidate. ALEPH experiment CERN |
Previous experiments provided a lower limit to the possible mass of the Higgs. It is not possible to compute the mass of the Higgs particle directly from theory. However, from precision measurements of the properties of other SM particles made at CERN, Fermilab SLAC and some other centres, it was possible to work backwards to a range of values for the Higgs mass. The LEP was able to test the possible Higgs mass range up to 114 GeV and the current consensus is that no convincing evidence for the existence of the Higgs particle was found below this energy, though several events were produced which could, possibly, be due to Higgs particle production and decay.
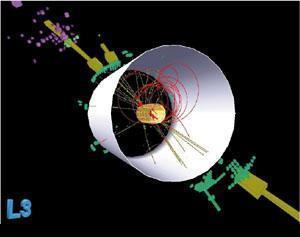
The event on the right, from the ALEPH detector, shows the decay of a candidate Higgs particle into four emerging sprays ("jets") of particles. The red/yellow pair and the blue/green pair emerge back to back, suggesting the production of a Higgs and a Z boson (for more information on this particular decay, see the Branching Ratios module). The image below shows a view of a candidate Higgs event from the L3 experiment. Some of the energy is dissipated as neutrinos and is therefore not visible.
|
|
Current measurements would place the mass of the Higgs particle at ~125.09 ± 0.21 (stat.) ± 0.11 (syst.) GeV (according to a combined analysis from ATLAS and CMS in 2015, found here). This is beyond the maximum energy which the LEP was able to test (approximately 114 GeV) and required the LHC experiments to be able to test with statistically significant accuracy.
For a Higgs particle at this energy, one of the most efficient ways to detect it is by looking for the decay of the Higgs into two high energy photons (gamma rays) rays (H → γγ). This gives a distinct signature in the detector chambers which can be used to identify the Higgs boson with little background interfering.
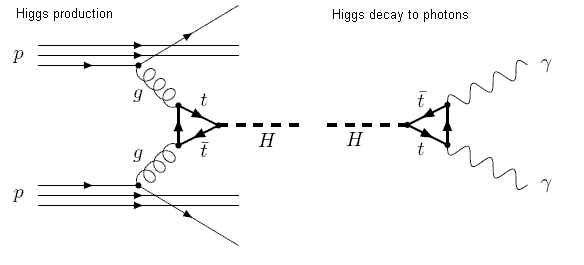
The Feynman diagrams below show possible production and decay paths for the Higgs. The Higgs only interacts directly with particles that have mass. In fact, the whole idea behind the Higgs is that its interactions actually cause those particles with mass to have mass in the first place. The Higgs cannot interact directly with massless particles such as photons and gluons. In a hadronic collision, the Higgs is produced in a two-gluon fusion process via a triangular loop of virtual top quarks. In the decay process, a loop of virtual top quarks allows the Higgs to decay into two photons.